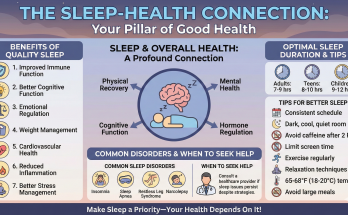
Mental health is just as important as physical health, yet it often goes overlooked. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore mental health awareness, stigma reduction, and strategies for building emotional resilience.
Understanding Mental Health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act, and influences how we handle stress, relate to others, and make choices.
The Prevalence of Mental Health Issues
Mental health disorders are more common than many realize. According to research, approximately 1 in 5 adults experience mental illness. Despite this prevalence, stigma prevents many from seeking help.
Common Mental Health Conditions
1. Depression
Characterized by persistent sadness, loss of interest, and feelings of hopelessness. It affects mood, sleep, appetite, and energy levels.
2. Anxiety Disorders
Include generalized anxiety, social anxiety, and panic disorder. Symptoms include excessive worry, fear, and physical manifestations like racing heart.
3. Bipolar Disorder
Characterized by extreme mood swings between manic and depressive episodes.
4. Schizophrenia
A complex disorder involving disruptions in thought processes, perceptions, and emotions.
5. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Develops after experiencing or witnessing traumatic events.
Breaking the Stigma
Mental health stigma creates barriers to seeking help and treatment. Breaking this stigma requires:
– Normalizing conversations about mental health
– Educating others about mental health conditions
– Challenging harmful stereotypes
– Supporting those with mental health challenges
– Using inclusive and respectful language
Warning Signs You May Need Help
– Persistent sadness or anxiety
– Significant changes in sleep or appetite
– Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
– Withdrawing from social activities
– Inability to handle daily tasks
– Thoughts of self-harm or suicide
– Substance abuse
Strategies for Mental Health and Resilience
1. Seek Professional Help
Therapists, counselors, and psychiatrists can provide evidence-based treatment.
2. Build a Support Network
Maintain connections with friends, family, and community.
3. Practice Self-Care
Engage in activities that promote well-being: exercise, hobbies, relaxation.
4. Develop Healthy Coping Skills
Learn stress management and problem-solving techniques.
5. Maintain Physical Health
Exercise, healthy eating, and adequate sleep support mental health.
6. Limit Negative Influences
Reduce exposure to toxic relationships and negative media.
7. Practice Gratitude and Mindfulness
These practices enhance emotional well-being and resilience.
When to Seek Immediate Help
If you or someone you know is experiencing suicidal thoughts or a mental health crisis, seek immediate professional help:
– Call a suicide hotline
– Go to the nearest emergency room
– Contact a mental health professional
– Reach out to a trusted person
Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness. Your mental health matters!